
Master Your Internal Linking Strategy for SEO Success
Sections
At its core, an internal linking strategy is simply the art of connecting pages on your own website to each other. Think of it like creating a detailed, logical map that guides both your visitors and search engine crawlers through your content, helping them understand how everything fits together and what’s most important. Getting this right is absolutely critical for SEO, as it spreads authority across your site and helps Google discover every last piece of valuable content you’ve created.
#Why An Internal Linking Strategy Matters More Than Ever
Imagine building a massive library filled with incredible, life-changing books. But here’s the catch: there are no signs, no catalog system, and no librarian to help anyone find what they’re looking for. That’s exactly what a website is like without a smart internal linking strategy. Your links are the unsung heroes of SEO, acting as the nervous system for your entire site. They’re the pathways that make everything work together as a cohesive whole.
A well-planned strategy transforms a confusing jumble of pages into an organized, authoritative resource. This isn’t about sprinkling links randomly wherever you can. It’s about designing a deliberate architecture that serves two very important audiences: search engines and your human visitors.
#Guiding Search Engine Crawlers
For search engines like Google, internal links are the main highways they use to discover and index your content. When a crawler lands on one of your pages, it follows the links it finds to navigate to other pages. Without these connections, you end up with “orphan pages” - valuable content that search engines might never even see because there’s no path leading to them.
A solid internal linking structure is also how you pass PageRank, or link authority, throughout your site. Pages that have earned powerful backlinks from other websites can share some of that SEO juice with other internal pages they link to. This helps lift the rankings of your entire website, not just a handful of star players. We cover more foundational concepts like this in our beginner’s guide to search engine optimization.
#Improving The User Journey
Now, let’s talk about people. For your human visitors, internal links simply create a better, more helpful experience. They provide useful context and guide users toward the information they need most, which naturally encourages them to stay on your site longer. This kind of engagement is a huge positive signal to Google that your content is valuable. When a user can effortlessly click from a broad topic to a more specific one, your site just feels more intuitive and trustworthy.
A well-planned internal linking strategy can help pass the value of high-quality backlinks from one page to another. In short: internal linking is key for any site owner that wants higher rankings in Google.
This whole process is also crucial for establishing what we call topical authority. By weaving a tight web of links between related articles, you’re sending a clear signal to search engines that you have deep expertise in a particular niche. It’s not just theory; some industry analyses suggest that a near-perfect internal linking setup is one of the quickest wins in SEO, often leading to a performance boost of 5-10%.
To put it all together, let’s look at the direct impact a great internal linking plan has on your website’s performance.
#How Internal Linking Impacts Your Website
| Benefit Area | Impact on SEO | Impact on User Experience |
|---|---|---|
| **Authority Distribution** | Spreads PageRank from high-authority pages to others, boosting their ranking potential. | Users are guided from general topics to specific, in-depth content, reinforcing trust. |
| **Content Discovery** | Ensures search engine crawlers can find and index all of your pages, preventing "orphan" content. | Makes it easy for visitors to find related information, keeping them on the site longer. |
| **Topical Relevance** | Establishes your site as an expert on a topic by creating a connected web of related content. | Provides helpful context and further reading, answering follow-up questions proactively. |
| **Site Navigation** | Creates a clear, logical site architecture that search engines can easily understand. | Improves the overall flow and usability of the website, reducing bounce rates. |
Ultimately, what’s good for the user is almost always good for SEO. A thoughtful internal linking strategy is one of the best examples of this principle in action, delivering tangible benefits for both sides of the coin.
#The Building Blocks of Effective Internal Links

Before you can build a truly powerful internal linking strategy, you have to get familiar with the raw materials. Think of it like a master builder who knows the exact purpose of every beam, brick, and joint. For an SEO, understanding each type of link is the first step toward creating a site structure that both people and search engines will love.
At the center of it all is a concept called link equity - you might have also heard it called “link juice.” It’s basically a vote of confidence. When a popular, respected page on your site links to another one, it passes along some of its authority. This transfer tells Google, “Hey, this page I’m pointing to is important, too.”
#The Different Types of Internal Links
Not all internal links are made equal. They each have a specific job to do and carry different weight in your overall strategy. Getting to know their roles is the key to using them like a pro.
There are three main types you’ll be working with:
-
Contextual Links: These are the gold standard. Found right in the body of your content - like in a blog post or on a service page - they are incredibly powerful for SEO because they’re surrounded by relevant text. Linking from a sentence about “keyword research techniques” to your in-depth guide on that exact topic gives Google a crystal-clear signal about what the destination page is about.
-
Navigational Links: These are the signposts of your website. Think of the permanent links in your main menu, footer, or sidebar. Their job is to create a consistent, predictable roadmap, helping users (and crawlers) easily find your most important pages, like “About Us,” “Services,” or “Contact.”
-
Breadcrumb Links: Ever seen those “you are here” maps in a shopping mall? That’s what breadcrumbs are for your site. They show users the exact path they took from the homepage to their current location, helping them understand where they are in your site’s hierarchy. This isn’t just great for user experience; it also clearly outlines your site structure for search engines.
Here’s a perfect example of what breadcrumb navigation looks like in the wild. It shows the user the exact hierarchical path to the page they’re on.

See how the path “Docs > Reference > Layout” instantly orients the user? It makes navigating back to a higher-level category a complete breeze.
#The Critical Role of Anchor Text
The final piece of the puzzle - and maybe the most important one - is anchor text. This is the visible, clickable text you see in a hyperlink. It’s so much more than just a placeholder; it’s a powerful signpost for both people and search engine algorithms.
Key Takeaway: Descriptive anchor text is one of the strongest signals you can send Google about a linked page’s content. Using vague phrases like “click here” or “read more” is a massive wasted opportunity.
Just look at these two examples. Which one is more helpful?
-
To learn more about optimizing your images, click here.
-
Properly formatting images is a key part of on-page SEO best practices.
The second option wins, hands down. It clearly tells you and Google what to expect on the other side of that click. While a contextual link tells Google that a page is important, the right anchor text tells it what the page is important for. Nail this, and you’ll have your internal links working overtime to help you rank for the keywords that matter most.
#How To Architect Your Site with Topic Clusters
Alright, let’s talk about building a website that search engines don’t just crawl, but actually understand. If you want Google to see you as an expert, you need to move past throwing links around randomly and start thinking like an architect. The best way to do this? The topic cluster model. It’s the gold standard for a modern internal linking strategy for a reason.
Think of your website like a solar system. At the very center, you have your sun - a huge, foundational pillar page covering a broad topic. Orbiting that sun are your planets - smaller, more focused articles, each diving deep into a specific subtopic. This structure creates a tight-knit web of content that signals serious expertise to Google while giving your readers a logical path to follow.
#The Anatomy of a Topic Cluster
This whole model hinges on two types of content working in harmony. Once you get the role each one plays, the strategy clicks into place.
-
Pillar Pages: This is your big, comprehensive guide. It covers a major topic from A to Z and targets a broad, high-volume keyword (think “digital marketing”). Your pillar page should be the definitive resource, linking out to all the more detailed articles.
-
Cluster Content: These are the deep-dive articles. Each one hones in on a specific subtopic and targets a more niche, long-tail keyword (like “social media marketing for restaurants” or “email marketing automation”). Crucially, every single one of these cluster pages must link back up to the main pillar page.
This isn’t a one-way street. The pillar links to the clusters, and the clusters link back to the pillar. It’s this two-way relationship that creates a powerful feedback loop, funneling authority and relevance right where you want it.
#Building Your Content Solar System
Putting this structure together isn’t as complicated as it sounds, but it does demand a clear plan. You can break it down into a few straightforward steps to start building your site’s authority, one topic at a time.
-
Identify Your Pillar Topics: First, brainstorm the core subjects you want your brand to be known for. These should be the big-picture ideas central to your business that also have real search interest. What are the main problems you solve for your customers? Start there.
-
Map Out Your Cluster Content: With a pillar topic chosen, start listing all the smaller, related subtopics that fall under its umbrella. This is where solid keyword research is your best friend. We cover how to dig up these specific, high-intent phrases in our guide to effective long-tail keyword research. Each of these subtopics is a potential cluster page.
-
Create the Linking Structure: As you create your content, be intentional with your links. Every time you publish a new cluster article, make sure it links back to your main pillar page with descriptive anchor text. Then, pop back over to your pillar page and add a link pointing to the new article you just published.
Key Insight: The topic cluster model transforms your site from a random collection of articles into a cohesive, organized library. It proves to search engines that your knowledge isn’t just wide; it’s also incredibly deep.
The diagram below gives you a simplified look at this hierarchy, showing how the homepage supports categories, which in turn support individual articles.
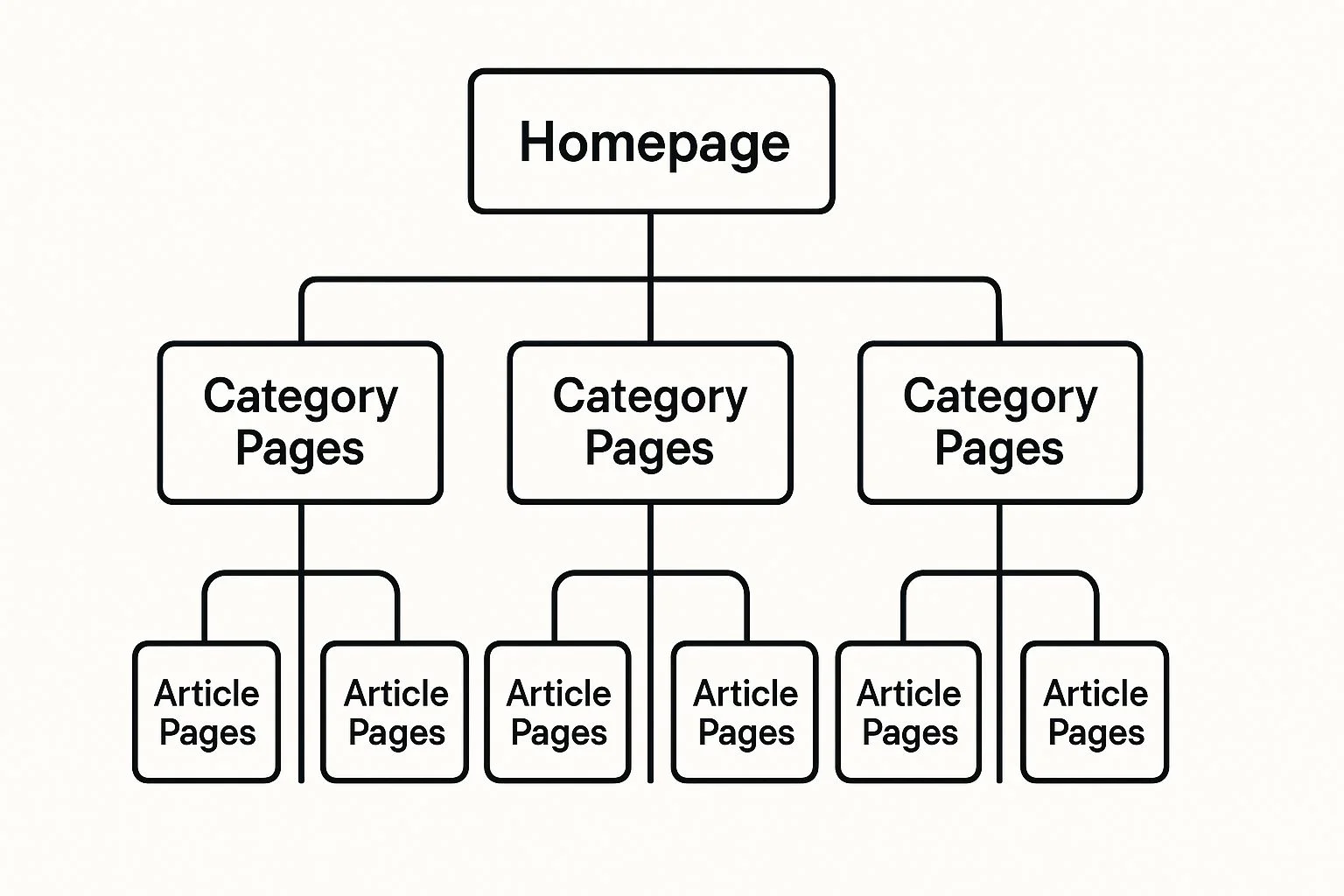
This visual shows exactly how authority flows downward, carving out a clear path for both your visitors and search engine crawlers. When you organize your site this way, you make it dead simple for Google to connect the dots and recognize your expertise. This, right here, is the foundation of an internal linking strategy that actually wins.
#Your Playbook for Executing an Internal Linking Strategy

Theory is great, but getting your hands dirty is what really moves the needle. This is where we shift from knowing about internal links to actually doing something with that knowledge. It’s time to create a repeatable process you can use every day to build a truly powerful internal linking strategy that fortifies your site from the inside out.
The goal here isn’t to just sprinkle links around randomly. Far from it. Every single link you place should have a clear purpose, whether it’s guiding a reader to the next logical piece of information or channeling authority to one of your most important pages.
Let’s jump into the most direct way to find those golden opportunities.
#Finding Opportunities with Precision
Believe it or not, one of the best tools for finding internal link opportunities is Google itself. A simple search command can instantly show you every single page on your site that mentions a specific topic. Just like that, you have a ready-made list of places to add a new link.
Let’s say you just published an incredible, in-depth guide on “content marketing.” To find all your existing articles that mention this phrase, just pop this into Google:
site:yourdomain.com "content marketing"
This one little trick gives you a list of older posts that are practically begging to be updated with a link to your new, authoritative guide. This doesn’t just give your new page a boost; it also makes your older content more valuable to anyone who lands on it.
#Mastering Your Anchor Text Game
Once you’ve found the perfect spot, your next move is to craft the right anchor text. This is the clickable text in the link, and it sends a massive signal to both users and search engines about what’s on the other side. A smart approach means diversifying your anchor text to give clear context without looking unnatural or spammy.
You’ll want to vary your anchor text to avoid looking like you’re trying too hard, which can sometimes raise red flags. It’s also about building a solid site structure with clear breadcrumb navigation and organizing your content into topic clusters. If you want to dive even deeper, check out the expert advice on internal linking best practices at TrafficThinkTank.com.
To help you get this right, let’s break down the different types of anchor text and when to use them.
#Choosing the Right Anchor Text for Your Links
Picking the right words for your links is a balancing act. You want to give search engines a clear signal about the linked page’s topic, but you also need to make sense to your human readers. This table breaks down your options, so you can choose the right tool for the job.
| Anchor Text Type | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| **Exact Match** | The anchor text is the exact target keyword of the page you're linking to (e.g., "social media tips"). | Use these sparingly to send a powerful relevancy signal to your most critical pages. |
| **Partial Match** | The anchor text includes the target keyword plus a few other words (e.g., "our guide on social media tips"). | Great for providing more context and naturally diversifying your anchor text profile. This is often your go-to. |
| **Branded** | The anchor text is simply your brand name (e.g., "Rankdigger's latest study"). | Perfect for when you're linking back to your homepage or a core brand page. |
| **Generic** | The anchor text is a common call to action (e.g., "read more" or "click here"). | Use these very rarely. They offer zero SEO context and should almost always be avoided in your main content. |
| **Naked URL** | The anchor text is the raw URL itself (e.g., [https://yourdomain.com/post](https://yourdomain.com/post)). | Best for citing sources or in situations where you want the URL to be visible and easy to copy. |
Ultimately, a healthy mix of these types looks the most natural to Google and provides the best experience for your users.
#Where to Place Links for Maximum Impact
Where you put a link on the page really matters. Sure, the links in your navigation menu and footer are crucial for site structure, but the real SEO powerhouses are the contextual links you weave directly into your content.
Key Insight: Links placed higher up in the body of your content tend to carry more weight with search engines. They’re also much more likely to be clicked by readers. A well-placed link in the first few paragraphs can do wonders for engagement.
Don’t treat linking as an afterthought you tack on at the end of an article. Instead, blend your links naturally into your paragraphs right where they add the most value and context for the reader. This creates a seamless journey, guiding them from one relevant piece of information to the next and keeping them on your site longer - a huge win for SEO.
Got the basics of internal linking down? Great. Now it’s time to level up. A truly powerful internal linking strategy isn’t just about connecting a few pages here and there. It’s about wielding those links with surgical precision. This is where you graduate from simple best practices and start using links to fix thorny SEO problems and multiply your biggest wins.
So many websites stumble here, making little mistakes that completely undermine their hard work. Things like broken links, pointing to irrelevant pages, or falling back on generic anchor text like “click here” can slowly poison your content’s value. To really get ahead, you have to sidestep these common traps and start using more advanced tactics.
#Fixing Keyword Cannibalization with Links
One of the most maddening issues in SEO is keyword cannibalization. This is what happens when several of your own pages are all trying to rank for the same keyword. It confuses Google, forcing it to guess which page is the most important. The result? Your authority gets split across multiple pages, and your rankings for that keyword take a nosedive.
Luckily, internal links are your best tool for cleaning up this mess. With a few careful adjustments, you can send a crystal-clear signal to search engines, telling them exactly which page should be the star for a specific keyword.
Here’s a quick game plan:
-
Pick Your Champion Page: First, decide which single page is your definitive authority on the topic. This should be your most comprehensive, highest-quality piece of content. Think of it as your “canonical” page.
-
Find the Contenders: Next, hunt down all the other pages on your site that are accidentally competing for that same keyword.
-
Reroute the Links: Go into those competing pages and change their internal links. Instead of linking out to various places, have them point directly to your champion page, using descriptive anchor text that includes the target keyword.
This process essentially tells Google, “Hey, I know these other pages touch on this topic, but this one right here is the real deal. Send all the ranking power to it.” It’s a strategic move that consolidates your link equity and makes your site structure much clearer to search engines.
#Funneling Authority to Your Power Pages
Let’s be honest: not all pages are created equal. Some pages on your site, which we can call “power pages,” have naturally attracted a ton of high-quality backlinks from other websites. These pages are SEO gold. They hold a massive amount of authority that you can, and should, spread around your own site. The goal is to find these valuable assets and use them to lift up other important pages that need a boost.
You can easily spot your most authoritative pages using SEO tools that analyze backlink profiles. Once you’ve got your list, start strategically adding internal links from these power pages to the pages you want to rank higher. This simple action funnels a slice of that hard-earned authority where it’s needed most, giving your priority content a serious lift.
A huge mistake is letting your most authoritative pages become dead ends. By linking from them to other relevant content, you create a powerful internal network that raises the tide for your entire site, not just one page.
Data absolutely supports this. An in-depth analysis of 23 million internal links found a direct link between having a healthy number of internal links and getting more search traffic. For example, pages with 40-44 internal links pulled in about four times more traffic than pages with only a handful. You can dig into the full internal linking study on zyppy.com to see all the details.
This tactic is a perfect partner to a well-rounded on-page SEO effort. For a complete guide on that, check out our on-page SEO checklist to make sure you’ve got all your bases covered. When you master these advanced methods, internal linking stops being a chore and becomes a proactive strategy for dominating the search results.
#Answering Your Internal Linking Questions
Even with the best plan in the world, once you start building out your internal linking strategy, real-world questions always pop up. It’s the little details that make the difference between a strategy that just works and one that truly excels.
Let’s dive into some of the most common questions that come up and give you clear, practical answers to help you make smarter decisions on the fly.
#How Many Internal Links Should Be on a Page?
Ah, the classic question. The truth is, there’s no magic number. The golden rule here is to always prioritize relevance and user value over sheer quantity. A few perfectly placed links that genuinely help a reader are infinitely more powerful than a page stuffed with dozens of random, forced links.
Think of it this way: every link you add should have a clear purpose. Does it help explain a tricky concept? Does it guide the user to the next logical step on their journey? If the answer is yes, then go for it. If you’re just trying to hit a quota, it’s best to skip it.
As a general guideline, keep these points in mind:
-
Keep It Natural: The number of links should feel organic and not forced. It should flow with the content.
-
Link Equity Dilution: While Google doesn’t have a strict limit, going overboard with links (think over 100) on a single page can water down the authority passed by each individual link.
-
A Practical Range: For most blog posts or articles, you’ll naturally land somewhere between 5 and 50 links. I’d avoid pushing past 75 internal links unless you’re dealing with a massive resource page where every single link is justified.
#Should I Link to My Homepage Often?
The short answer? Probably not from the main body of your content.
Your website’s logo and the main navigation menu already do a great job of linking back to your homepage from every single page on your site. That’s usually more than enough. When you’re adding contextual links within your articles, your goal is to strengthen specific, topically related pages.
Sending that link equity to your homepage is often a wasted opportunity. You’re much better off pointing it toward a core pillar page or a relevant cluster article that provides more focused information. Save those direct homepage links for the rare moments when it’s genuinely the most relevant place to send a user.
#What Is the Difference Between Internal and External Links?
This is one of those fundamental concepts in SEO, and it’s crucial to get it right. Both are hyperlinks, of course, but they serve completely different functions and have a very different impact on your site’s authority.
Key Distinction: Internal links keep users and link equity circulating within your website, strengthening its structure. External links send users and link equity away from your site, usually to cite a source or provide extra resources.
Let’s quickly compare them side-by-side to make the roles crystal clear.
| Feature | Internal Links | External Links |
|---|---|---|
| **Destination** | Connects one page on your site to another page on the **same website**. | Points to a page on a completely **different website**. |
| **Primary Goal** | To improve site navigation, spread authority (PageRank) internally, and guide users through your content funnel. | To cite sources, provide additional information, and build credibility by referencing other authoritative sites. |
| **SEO Impact** | Helps Google crawl your site, understand its structure, and establish your topical authority. | Passes link equity away from your site (unless you use "nofollow") and can boost your content's trustworthiness. |
For instance, if I link from this blog post to our about page, that’s an internal link. If I link out to a research study from a university, that’s an external link. Simple as that.
#How Do I Fix Broken Internal Links?
Broken internal links are silent killers for both user experience and SEO. They lead visitors and search engine crawlers to dead ends - those frustrating 404 error pages - which wastes precious link equity and annoys your audience. Regularly finding and fixing these is a non-negotiable part of website maintenance.
Luckily, the process is pretty straightforward once you have the right tools.
-
Find the Broken Links: First, you need to find them. You can use a tool to crawl your entire site and spit out a list of any internal links pointing to pages that don’t exist. Google Search Console (check under “Pages” > “Not found (404)”), Ahrefs’ Site Audit, or Screaming Frog are all fantastic for this.
-
Assess the Broken URL: Once you have your list, you just need to figure out the best way to fix each one.
-
Update or Redirect: You’ve got two main choices here. If the link was just a typo or the page’s URL was recently updated, you can simply update the link to point to the correct, live page. If the original page was deleted on purpose, your best bet is to set up a 301 redirect from the old, broken URL to the next most relevant page on your site. This makes sure any authority that link was passing gets redirected, not lost.
Fixing these errors guarantees a smooth ride for your users and helps search engines crawl your site much more efficiently. It’s a simple cleanup that ensures no authority gets left on the table.
Ready to stop guessing and start seeing real results from your SEO efforts? Rankdigger provides the intuitive dashboards and advanced analytics you need to build a winning internal linking strategy. Use our free Search Analytics tool to uncover your most valuable pages and discover high-potential keywords to supercharge your growth. Explore Rankdigger and take control of your SEO today.

